What Is a Good Credit Score?
A good credit score can help you get approved for attractive rates and terms when you apply for a loan. But determining whether a particular credit score is good or not is complicated. This is because the extent of what is considered good may vary depending on the type of loan you are applying for and which lender is reviewing your information. Join different lenders’ mixes using different credit scoring models, and your score is likely to end up depending on which method was used.
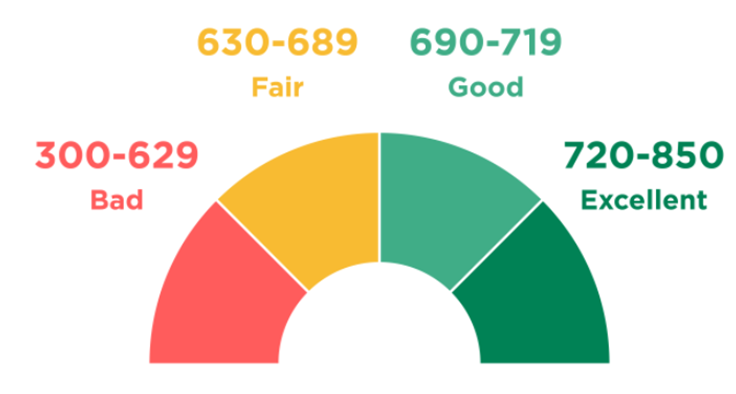
When you apply for new credit, you are not told what the exact cut-off point of this particular lender is between a good credit score and a bad one. This is because lenders generally do not disclose the limits of their credit score to the public. Nevertheless, FICO, the most popular credit scoring model, shares some helpful information that lenders can use as a guide. The most common FICO scores range from 300 to 850. On this scale, a credit score between 670 and 739 is generally considered “good.”
What is a good FICO® score?
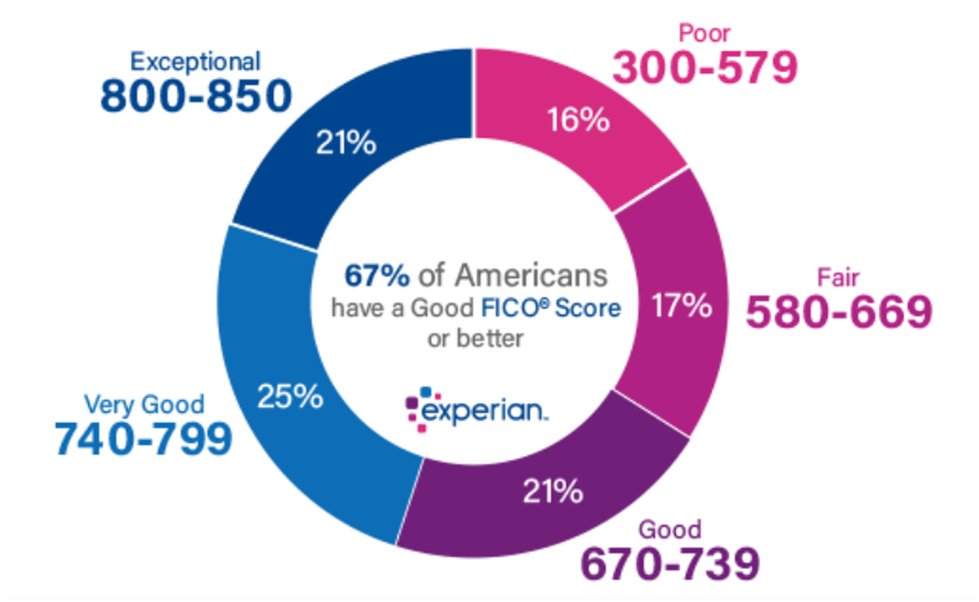
FICO® builds credit scores for different types of users. “Base” is FICO® scores that the company develops for use by lenders in a variety of industries, as well as industry-specific credit scores for credit card issuers and auto lenders.
The basic FICO® scores range from 300 to 850, and the FICO sets the “good” range from 670 to 739. FICO®’s industry-specific credit scores range from 250 to 900. However, the middle categories are the same. The specific FICO® score related to grouping and a “good” industry is still 670 to 739.
What is a good VantageScore?
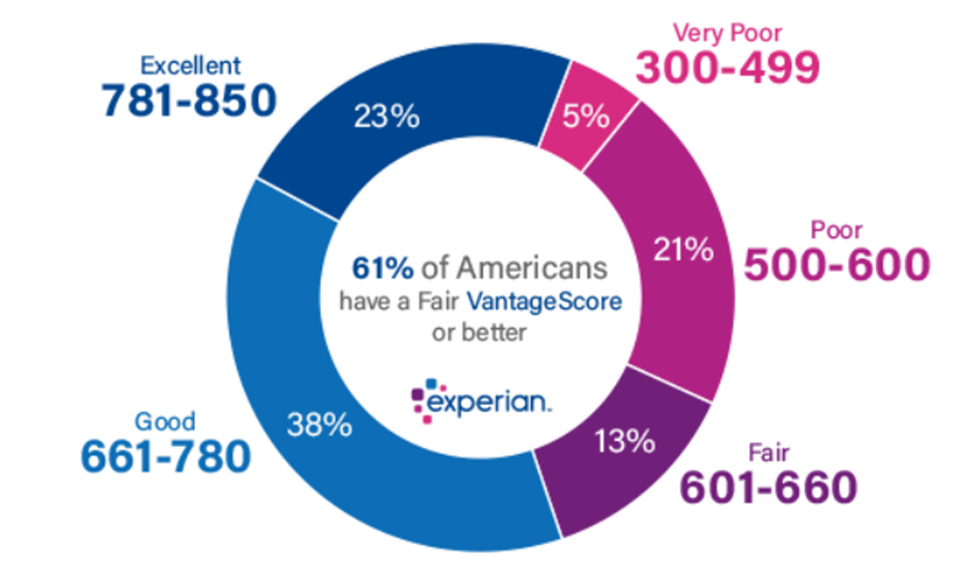
VantageScore’s first two credit scoring models ranged from 501 to 990. The two most advanced VantageScore credit scores (VantageScore 3.0 and 4.0) use a range of 300 to 850, which is the base FICO® score. For the latest models, VantageScore describes the 661 to 780 as its good range.
How does it affect your credit score?
Common factors can affect all of your credit scores, and they are often divided into five categories:
- Payment History: Paying on time on your credit accounts can help your score. But filing a missing payment, an account sent for deposit, or bankruptcy can damage your score.
- Use of Credit: How many accounts you have balances, how much you owe, and the portion of your credit limit you are using on revolving accounts, all work here.
- Length of Credit History: This category includes the average age of all your credit accounts, as well as the age of your oldest and newest accounts.
- Types of Accounts: Also called “credit mix”, it considers whether you have two installment accounts (such as car loan, personal loan, or mortgage) and revolving accounts (such as credit cards and credit lines). Are managing other types of). Showing that you can manage both types of accounts responsibly usually helps your score.
- Recent Activity: It considers whether you have recently applied for or opened new accounts.
FICO® score factors
FICO® typically uses percentages to indicate how important each category is, although the exact percentage error used to determine your credit score will depend on your unique credit report. FICO® considers scoring factors in the following order:
- Payment Date: 35%
- Amount due: 30%
- Length of credit history: 15%
- Credit mix: 10%
- New credit: 10%
Vintage score factors
VantageScore lists the factors that are generally influential in determining your credit score, but it will also depend on your unique credit report. VantageScore considers factors in the following order:
- Total Credit Usage, Balance, and Available Credit: Highly Effective
- Credit mix and experience: Extremely influential
- Payment date: Affect moderation
- Age of Credit History: Less Influential
- New accounts opened: less influential
What Factors Affect Your Credit Score?
Here are some tried and true attitudes to keep in mind when you start establishing or maintaining responsible credit attitudes:
- Each time, pay your bills on time. This does not only include credit card delays or denial of payments to other accounts, such as cell phones, which can be reported to the credit bureau and can affect your credit score. If you are having trouble paying the bill, contact the lender immediately. Don’t skip payments, even if you disagree on a bill.
- Pay off your debts as soon as possible.
- Keep your credit card balance below the limit. A balance higher than your credit limit can affect your credit score.
- Apply for a little credit. Applying for multiple credit accounts in the short term can affect your credit score.
- Check your credit reports regularly. Request a free copy of your credit report and check to make sure your personal information is correct and that there are no invalid or incomplete account information. You are entitled to a free copy of your credit reports every 12 months from each of the nationwide credit bureaus by visiting www.annualcreditreport.com. By requesting one copy every four months, you can keep track of your reports throughout the year. Remember: Checking your own credit report or credit score will not affect your credit score.
You can also create an Equifax account to receive six free Equifax credit reports each year. Additionally, you can click on “Get My Free Credit Score” on your myEquifax dashboard to enroll in Equifax Core Credit for a free monthly Equifax credit report and free monthly VantageScore® 3.0 credit score based on Equifax data. can. VantageScore is one of the many types of credit score.
Bottom line
If you are wondering how important it is to earn and maintain a good credit score, the short answer is yes. When you work hard to get a good credit score, the savings can be substantial. The lifetime value of a good credit score can go up to tens of thousands of dollars.
If you find information that you think is incorrect or incomplete, contact the lender or lender. You can also file a dispute with the credit bureau that submitted the report. On Equifax, you can create my Equifax account to file a dispute. See our Disputes page for other ways to submit a dispute.